
Have you been told you have gum disease—or suspect you might—and you’re wondering if there’s a way to truly cure it? Periodontal disease is a condition that affects millions of people, yet there’s still confusion about whether it can be fully reversed or only managed. Let’s dive into the facts.
Understanding the truth about periodontal disease can help you protect your oral health for life. Whether you’re in the early stages or dealing with more advanced issues, knowing your options and how to stop the disease in its tracks is crucial.
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It begins as gingivitis—mild gum inflammation—and can progress to periodontitis if left untreated. In its advanced stages, periodontal disease can lead to tooth loss and systemic health problems. It is primarily caused by bacterial plaque buildup, but genetics, smoking, and poor oral hygiene also play a role. Understanding this condition is the first step in taking control of your oral health and exploring whether it can be cured or effectively treated.
Symptoms and Causes of Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is typically caused by poor oral hygiene that allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth and gums. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding when brushing or flossing. Though often mild, it’s a warning sign that your gums are under stress. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with prompt professional care and improved daily oral hygiene.
Periodontitis, on the other hand, is a more advanced and serious form of gum disease that develops when gingivitis goes untreated. Bacteria spread below the gumline, causing chronic inflammation and the breakdown of tissue and bone that support the teeth. Symptoms include persistent bad breath, gum recession, loose teeth, swollen gums, and discomfort while chewing. Unlike gingivitis, periodontitis requires ongoing professional treatment to manage and prevent further damage.
Is Periodontal Disease Curable or Just Treatable?
Periodontal disease is not considered curable, especially in its advanced stages, but it is highly treatable and manageable. While early-stage gum disease can be reversed with proper care, periodontitis requires ongoing professional treatment to control the infection and prevent further damage. With consistent oral hygiene, lifestyle adjustments, and expert periodontal care, most patients can successfully manage the disease and maintain healthy teeth and gums for life.
Can Gingivitis Be Cured?
Yes, gingivitis can be completely cured, especially when caught early. Since it only affects the surface layers of the gums and hasn’t yet caused permanent damage, professional cleanings combined with improved daily oral care can fully reverse the condition. With consistent brushing, flossing, and routine dental visits, healthy gums can be restored in a matter of weeks.

Periodontal Disease Treatments
Treating gum disease depends on the severity of the condition and how far it has progressed. While early-stage gingivitis can often be reversed with non-invasive treatments, more advanced gum disease may require surgical intervention. Let’s explore both types of treatment options commonly used by periodontists to manage and control gum disease.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense against gum disease, especially in its early to moderate stages. These procedures aim to control bacterial growth, reduce inflammation, and stop the progression of the disease without the need for incisions or sutures. Here are the most common non-surgical options:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep dental cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from tooth surfaces and roots, often reaching below the gumline. It helps smooth the root surfaces, making it harder for bacteria to reattach and cause further inflammation.
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Patients are coached on effective brushing and flossing techniques and may be advised to use antimicrobial mouthwashes. These at-home practices are essential in supporting in-office treatments and preventing recurrence.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics—whether topical gels, mouth rinses, or oral pills—are prescribed to eliminate lingering bacterial infections that haven’t responded to other methods.
- Laser Bacterial Reduction (LBR): This low-level laser treatment is used to target and reduce bacteria around the gums during non-surgical visits. Often performed alongside scaling and root planing, it enhances healing and decreases inflammation without incisions or tissue removal.
Surgical Treatments
When non-surgical methods are not enough to halt the progression of gum disease, surgical treatment may be necessary, especially at a higher level of periodontitis. These periodontal treatments are designed to restore damaged tissues, reduce deep pockets, and regenerate bone and gum support. Below are some of the most effective surgical techniques used in periodontal therapy:
- Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): This procedure involves lifting the gums to access deep pockets of plaque and tartar. After thorough cleaning, the gums are repositioned snugly around the teeth to reduce pocket depth and limit future bacterial buildup.
- Bone Grafting: When bone loss has occurred due to periodontitis, bone grafts can help restore stability. This procedure uses natural or synthetic bone to encourage regrowth and provide support for teeth or future implants.
- Gum Grafting: Gum grafts are used to cover exposed roots and rebuild receding gum tissue. This not only improves appearance but also protects the roots from sensitivity and decay.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR): In cases of severe bone loss, GTR uses a biocompatible membrane to encourage the regrowth of bone and tissue while keeping unwanted cells out of the healing area.
- Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure (LANAP): This advanced, minimally invasive laser surgery targets infected gum tissue while preserving healthy areas. It stimulates tissue regeneration and promotes new attachment of the gums to the teeth.
How to Keep Periodontal Disease Under Control
Keeping gum disease under control requires a long-term commitment to healthy habits and follow-up care. By making the right choices every day, patients can successfully manage their condition and prevent it from progressing.
Daily Oral Health Tips
Consistent and thorough oral hygiene is the foundation for keeping periodontal disease in check. Proper brushing and flossing habits help remove plaque before it can harden into tartar and irritate the gums. Patients with a history of gum disease must be especially vigilant with these daily routines.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors
What you eat and how you live plays a direct role in your gum health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, along with antioxidants, can help support the immune system and reduce inflammation. Additionally, avoiding tobacco use, managing stress, and staying physically active all contribute to a healthier mouth and stronger resistance to periodontal disease.
Before & After Photos
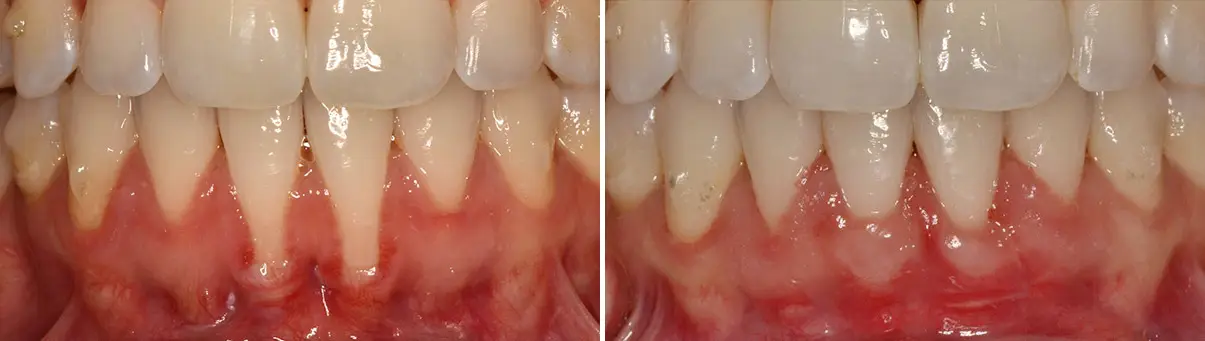
* All patients are unique and individual results may vary.
The Link Between Periodontal Disease and Other Health Conditions
Periodontal disease causes more than just oral health issues. Gum disease germs can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation elsewhere, producing a variety of health issues.
Gum Inflammation Can Cause Diabetes
Research has shown a bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes. Poor glycemic control can result from gum inflammation, which makes it harder for diabetics to control their blood sugar levels. In contrast, gum disease is more likely to occur in people with high blood sugar levels.
Chronic Inflammation Can Increase the Risk of Cancer
Chronic inflammation, a common characteristic of periodontal disease, has been linked to an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as oral, pancreatic, and colorectal cancer. By managing periodontal disease and reducing inflammation, you may lower your chance of developing these cancers.
Living with Periodontal Disease Can Affect Pregnancy
Periodontal disease has been associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as low birth weight and preterm birth. Pregnant women with gum disease are at a higher risk of delivering premature babies and babies with low birth weight. Maintaining good oral health during pregnancy is crucial for both the mother’s and the baby’s well-being.
Living with Periodontal Disease Can Affect Respiratory Health
Problems with respiratory health like pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have been linked to periodontal disease. Gum disease-related dangerous bacteria found in the mouth can be breathed into the lungs and cause inflammation and illnesses there. Therefore, keeping proper dental hygiene helps to lower the danger of respiratory health problems by means of which one can avoid troubles.
Gum Disease Increases Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease
Recent studies have found a connection between periodontal disease and an increased risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. The inflammation caused by gum disease may contribute to the degeneration of brain cells, leading to cognitive decline. Maintaining good oral health and addressing periodontal disease early can help protect your brain health and reduce the chance of developing these neurodegenerative diseases.
What to Look for in a Dentist or Periodontist
When it comes to managing and treating periodontal disease, experience truly matters. A skilled specialist understands the complexities of gum health and offers solutions that go beyond surface-level care. With the right expert, patients can prevent tooth loss, avoid recurring infections, and achieve long-term oral health.
With an unwavering dedication to the field of periodontics, Dr. John Paul Gallardo, DDS, PA, stands as South Florida’s leading periodontist and implant specialist. With over 25 years of experience, Dr. Gallardo is known for his meticulous attention to detail and cutting-edge techniques that deliver life-long results.
At Gallardo Periodontics and Implant Dentistry, our state-of-the-art Miami facility ensures safe, effective care with options like IV conscious sedation for a comfortable experience. Ready to take the first step? Call us at 305-447-1447 or visit our contact page to schedule a consultation.
Common Questions About Gum Disease
Is periodontal disease contagious?
Periodontal disease is not contagious in the way a cold or flu is, but the bacteria that contribute to it can be transmitted through saliva. Sharing utensils, kissing, or other forms of close contact can transfer harmful oral bacteria. However, simply being exposed to these bacteria doesn’t guarantee infection—it typically requires poor oral hygiene or a compromised immune system for the disease to take hold.
Can gum tissue grow back after treatment?
Gum tissue that has receded due to periodontal disease typically does not grow back on its own. However, certain treatments like gum grafting and guided tissue regeneration (GTR) can help restore lost tissue in targeted areas. These procedures are most effective when combined with good oral hygiene and regular periodontal care to prevent further damage.
What are the risk factors of gum disease?
Several factors can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. Poor oral hygiene, smoking or tobacco use, genetics, hormonal changes, certain medications, and underlying health conditions like diabetes all play a role. Even stress and poor nutrition can weaken your immune response, making it harder for the body to fight off gum infections.
How long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?
With proper treatment and ongoing care, many patients with periodontal disease can keep their natural teeth for a lifetime. The key is early intervention, consistent oral hygiene, and regular visits to a periodontist. Even in more advanced cases, professional management can slow or stop the disease’s progression and preserve tooth stability.