
Receding gums is a common condition affecting the soft tissue of your gums. It occurs when the gum tissue around the base of your teeth wears away, exposing more of the tooth root. This can be caused by periodontal disease, brushing your teeth too vigorously or using a hard-bristled toothbrush.
When left untreated, receding gums can lead to serious oral health issues such as tooth loss and sensitivity. Periodontal disease is a major cause of gum recession. This bacterial infection destroys the bone and other tissues that support your teeth in their sockets and may result in inflamed and receding gums. Additionally, aggressive brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can contribute to receding gums by eroding away at the soft tissue surrounding your teeth.
If you suspect you have receding gums, it’s important to visit your dentist or periodontist for an evaluation right away. Your dentist will examine your mouth to assess how far the recession has progressed and recommend treatment options accordingly. In some cases, a deep cleaning may be necessary to remove plaque and tartar buildup beneath your gum line that’s causing inflammation and gum recession. If this isn’t enough to stop further damage from occurring, surgery may be recommended to repair any compromised gum tissue or replace bone lost due to periodontal disease
Receding gums is a serious issue that should not be taken lightly as it can lead to severe pain, sensitivity, and even tooth loss if left untreated for too long. If you think you may have receding gums or are experiencing any signs associated with it such as redness or tenderness in your gums, contact your dentist right away for an evaluation so they can determine which treatment option is best for you.
Causes of Receding Gums
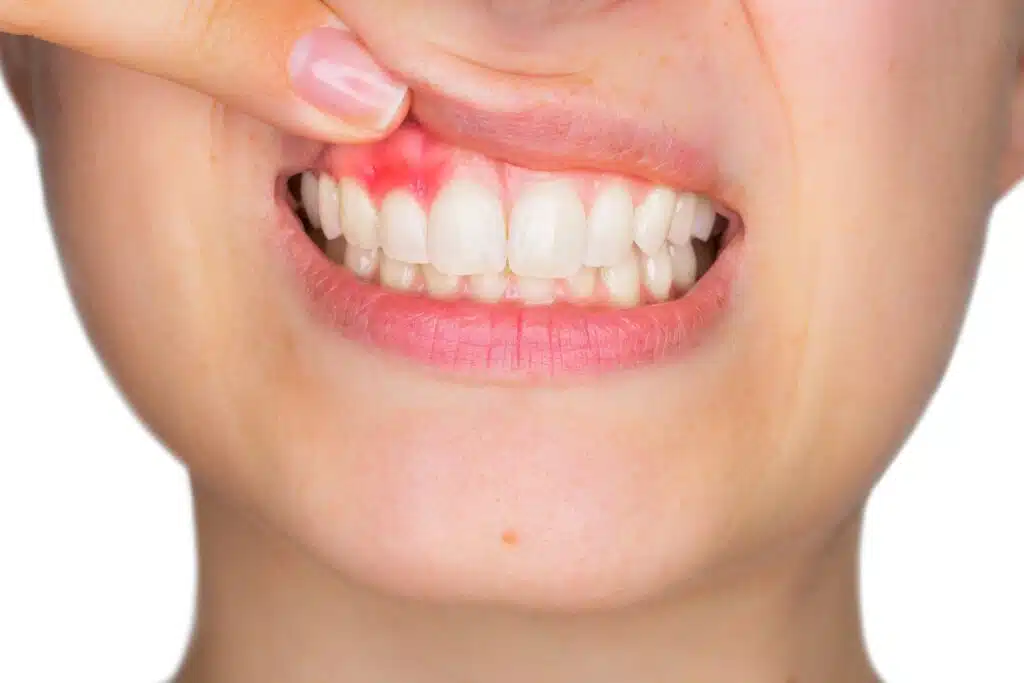
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is a common condition that affects the soft tissue of your mouth. It occurs when the gum tissue around the base of your teeth wears away, exposing more of the tooth root. The main causes of receding gums are periodontal disease, loose teeth, misaligned teeth, and harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that destroys supporting bone and other tissues surrounding your teeth in their sockets and results in inflamed and receding gums. Loose teeth can be caused by trauma or periodontal disease which often leads to recession of your gums. Misaligned teeth can cause extra pressure on certain areas of your mouth which can result in gum erosion over time. Harmful bacteria such as plaque and tartar buildup underneath your gum line may also lead to receding gums if left untreated for too long.
If you think you may have receding gums it’s important to visit an oral surgeon or periodontist right away for an evaluation so they can identify how far the recession has progressed and recommend treatment options accordingly. Depending on how severe the condition is, treatment may include dental cleanings, gum grafts or other dental treatments to repair damaged tissue or replace bone loss due to periodontal disease.
Signs and Symptoms of Receding Gums
Diagnosis of Receding Gums
The diagnosis of receding gums typically begins with a thorough examination of the patient’s gum health and any other dental issues that may be present. During the exam, your periodontist will carefully measure the gingival margin to determine if there is loss of gum tissue and also look for signs of inflammation or infection in the area. To identify how far the recession has progressed, X-rays or other imaging studies may be taken to assess any damage to the underlying bone and connective tissue.
Once a diagnosis is made, a treatment plan can be formulated depending on how severe the recession is. If caught early enough, it may only require a deep cleaning or tooth scaling to remove plaque and tartar buildup beneath your gum line that’s causing inflammation. However, if severe damage has already been done then more extensive treatments such as gum grafting or periodontal surgery may need to be performed in order to repair damaged tissue or replace lost bone caused by periodontal disease.
No matter which treatment option is chosen for your individual situation, it’s important to follow your periodontist’s instructions closely in order to ensure successful outcomes from your gum treatment plan. Taking good care of your oral health is essential when dealing with receding gums so make sure you are brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly as well as scheduling regular visits with your dentist for checkups and cleanings.
Prevention of Receding Gums
Preventing receding gums is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing the onset of painful, sensitive gum recession. Having healthy gums free from periodontal disease is key to avoiding the common signs of receding gums, such as redness or tenderness in the area. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are important for keeping your gums and teeth healthy, as well as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly.
Using an electric toothbrush can also help prevent gum disease by providing a more thorough clean than manual brushing does, while using an antibacterial mouthwash after brushing can help reduce the amount of harmful bacteria in your mouth that can cause periodontal disease. In addition, it’s important to watch out for any other medical conditions that may be causing gum recession such as diabetes or hormonal imbalances that can make it difficult to keep your gums healthy.
If you think you may have signs of receding gums or are experiencing any symptoms associated with them such as sensitivity or pain in your teeth, contact your dentist right away for an evaluation so they can determine which treatment option is best for you. Early diagnosis and proper oral care are essential when it comes to preventing and successfully treating receding gums so don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you suspect something may be wrong with your gums. Your dentist will cover from alloderm cost to after care tips.

Regular Dental Checkups and Cleanings
Regular dental checkups and cleanings are an important part of preventing receding gums. During a routine exam, a periodontist or other dental specialist will carefully assess the gum health, looking for any signs of inflammation or infection. A thorough cleaning is also important to remove plaque and tartar buildup that can cause receding gums. Hard-to-reach areas may be inspected using imaging technology such as X-rays or clinical trial studies to detect any damage to underlying bone structures and connective tissue.
If noticeable symptoms like redness or tenderness in the area are present during the exam, your dentist may recommend treatments such as scaling or deep cleaning to help prevent further recession. Following your dentist’s instructions for oral health care is also essential for keeping your gums healthy. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, and using an electric toothbrush can all help maintain healthy gum tissue and keep your mouth free of harmful bacteria that can lead to periodontal disease.
Treatment Options for Receding Gums
Treatment options for receding gums vary depending on the severity of the condition, but can range from simple lifestyle changes and regular dental care to more involved procedures such as gum surgery. Eating a healthy diet, practicing good dental hygiene, and scheduling regular checkups with your dentist can help prevent the occurrence of gum recession in the first place. If you are already experiencing signs of gum recession such as redness or tenderness in the area, your dentist may recommend one or more of the following treatments:

Flap Surgery
During flap surgery, your periodontist will lift up part of the gum tissue to expose teeth roots before reshaping them to cover any exposed areas. This procedure is commonly used to restore lost gum margin as well as treat pockets that have formed due to periodontal disease.
Gingival Grafts
Gingival grafts are often used when traditional flap surgery is not an option due to insufficient healthy tissue available in the area. During this procedure, a piece of healthy tissue will be taken from another area in your mouth and grafted over affected areas.
Orthodontic Treatment
In cases where receding gums have been caused by misaligned teeth or malocclusion, orthodontic treatment may be recommended to correct these issues and reduce further loss of gum margin. Braces or clear aligners may be used to reposition teeth and restore healthy gingival tissue back into its original position.
Bone Regeneration
Bone regeneration is a surgical procedure that aims to restore lost bone supporting the teeth. This involves placing a bone graft material in the affected area, which stimulates the body’s natural ability to regenerate bone tissue. This treatment is particularly beneficial for patients with severe gum recession caused by advanced periodontal disease.
Tissue Grafts
Tissue grafts involve taking soft tissue, usually from the roof of the mouth, and transplanting it to the area where the gums have receded. This procedure helps cover exposed roots, reduce sensitivity, and improve the overall appearance of the gums. There are different types of tissue grafts, including:
- Connective Tissue Grafts: Commonly used to treat root exposure around one or more teeth.
- Free Gingival Grafts: Utilized to thicken gums and treat thin or receding gums.
- Pedicle Grafts: Involves grafting tissue from the gum near the tooth needing repair, useful for patients with plenty of gum tissue near the tooth.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
This technique involves placing a small piece of mesh-like fabric between the bone and gum tissue. The mesh prevents the gum tissue from growing into the area where the bone should be, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow and better support the teeth.
Pinhole Surgical Technique
A minimally invasive procedure where a small hole is made in the gum tissue, and special instruments are used to loosen the gum tissue and slide it over the receded part of the tooth. This technique reduces discomfort and recovery time compared to traditional grafting methods.
Laser Therapy
Laser-assisted new attachment procedure (LANAP) uses lasers to remove diseased gum tissue and kill bacteria. This technique can promote the reattachment of healthy gum tissue to the teeth and regenerate lost bone.
No matter which treatment option is chosen for your individual situation, it’s important to follow your periodontist’s instructions closely in order to ensure successful outcomes from your gum treatment plan. Taking good care of your oral health is essential when dealing with receding gums so make sure you are brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly as well as scheduling regular visits with your dentist for checkups and cleanings.
Before & After Photos
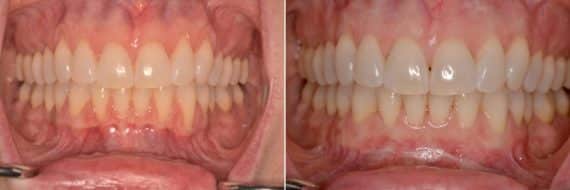
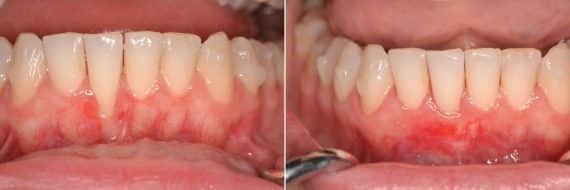
* All patients are unique and individual results may vary.
Complications Associated with Receding Gums
Receding gums can have a serious impact on an individual’s oral health. Complications associated with receding gums include infected tissue, the need for surgical treatment, and other oral surgery. The condition usually occurs when the gum line is pulled away from the teeth, leaving teeth vulnerable to decay and bacteria build-up. As periodontal disease progresses, it can lead to further deterioration of gum tissue and even tooth loss.
When you have receding gums, the sooner you see a dentist or periodontist and get treatment, the better. In the Miami area, Dr. John Paul Gallardo are available to discuss your treatment options and to provide guidance on ways to prevent further recession from occurring. To schedule an appointment with the periodontists, call (305) 447-1447 today.
Frequently Asked Questions on Receding Gums
Receding gums can present several symptoms, including:
Sensitivity to hot and cold
Teeth appearing longer than usual
Visible roots
Swelling or redness of the gums
Bleeding after brushing or flossing
Gums do not naturally grow back once they have receded. However, treatments like gum grafting can help restore gum tissue.
Common causes include periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, tobacco use, teeth grinding, and genetics.
Preventive measures include maintaining proper oral hygiene, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, regular dental check-ups, a healthy diet, quitting smoking, addressing teeth grinding, and avoiding oral piercings.
Yes. Treatments include professional cleaning, scaling and root planing, gum grafting, and advanced techniques like guided tissue regeneration and the pinhole surgical technique.